

| Deutsche Version |
● Convert Decibels to Voltage Gain / Loss ●
● Convert Voltage Gain / Loss to Decibels ●
• Voltage and Gain •
| Enter any two values - the third will be calculated. |
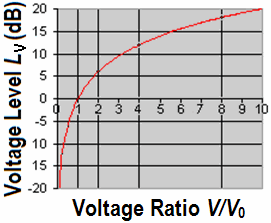 |
V0 = 1 Volt |
| To use the calculator, simply enter a value. The calculator works in both directions of the ↔ sign. |
Gain and Loss
|
Gain is: 1) A knob usually found at the top of each input channel on the sound board, used to set input levels of the separate channels to relatively equal positions. 2) The amount of increase in audio signal strength, often expressed in dB. Gain:The measure of how much a circuit amplifies a signal. Gain may be stated as Conductive Hearing Loss: a loss of sensitivity to sound, resulting from an Gain or Loss: These are reciprocal numbers; they will be given in several ways. dB (decibel): A technique for expressing voltage,power, gain, loss, or frequency in Voltage Controlled Attenuator (VCA): |
|
Sound level, loudness, and sound pressure are not the same things. There are variations in individual perception of the strength of sound. The sound pressure measured twice as much gives 6 dB more level. The sound perceived twice as loud needs roughly an increase in sound level by 10 dB. |
Common Gains and Losses Expressed in Decibels
Notice: Power gain is not used in audio engineering.
| Gain/loss as a ratio (out/in) |
Gain/loss as a factor |
Gain/loss in dB Field sizes (Voltage gain) |
Gain/loss in dB Energy sizes (Power gain) |
| 10,000:1 | 10,000 | +80.00 dB | +40.00 dB |
| 1,000:1 | 1,000 | +60.00 dB | +30.00 dB |
| 100:1 | 100 | +40.00 dB | +20.00 dB |
| 10:1 | 10 | +20.00 dB | +10.00 dB |
| 5:1 | 5 | +13.98 dB | +6.99 dB |
| 4:1 | 4 | +12.04 dB | +6.02 dB ● |
| 2:1 | 2 | +6.02 dB ● | +3.01 dB |
| 1:1 | 1 | 0,00 dB | 0.00 dB |
| 1:2 | 0.5 | −6.02 dB ● | −3.01 dB |
| 1:4 | 0.25 | −12.04 dB | −6.02 dB ● |
| 1:5 | 0.2 | −13.98 dB | −6.99 dB |
| 1:10 | 0.1 | −20.00 dB | −10.00 dB |
| 1:100 | 0.01 | −40.00 dB | −20.00 dB |
| 1:1,000 | 0.001 | −60.00 dB | −30.00 dB |
| 1:10,000 | 0.0001 | −80.00 dB | −40.00 dB |
40 dB voltage gain (amplitude) is 100 times the voltage factor (amplitude).
40 dB power gain is 10,000 times the power factor.
Voltage Gain = Voltage Amplification and Power Gain = Power amplification
| Voltage (amplitude) gain | Power (energy) gain | |||
| Voltage ratio Factor V2/V1 |
Voltage amplification GV in dB |
Power ratio Factor P2/P1 |
Power amplification GP in dB |
|
| 103 | +60 | 106 | +60 | |
| 102 | +40 | 104 | +40 | |
| 101 | +20 | 102 | +20 | |
| √10 = 3.16 | +10 | 10 | +10 | |
| 2 | +6 | 4 | +6 | |
| √2 = 1.414 | +3 | 2 | +3 | |
| 1 | ±0 | 1 | ±0 | |
| 1/√2 = 0.7071 | −3 | 1/2 = 0.5 | −3 | |
| 1/2 = 0.5 | −6 | 1/4 = 0.25 | −6 | |
| 1/√10 = 0.316 | −10 | 10−1 = 0.1 | −10 | |
| 10−1 = 0.1 | −20 | 10−2 = 0.01 | −20 | |
| 10−2 = 0.01 | −40 | 10−4 = 0.0001 | −40 | |
| 10−3 = 0.001 | −60 | 10−6 = 0.000001 | −60 | |
| V2/V1 = 10(GV in dB/20) | GV = 20×log (V2/V1) | P2/P1 = 10(GP in dB/10) | GP = 10×log (P2/P1) | |
 |
|
| Questions: For an amplifier with an amplification factor of 100, calculate the following: a) voltage gain in dB. b) voltage gain at the cutoff frequency (break frequency) in dB. c) amplification factor at the cutoff frequency (break frequency). Answers: a) amplification factor 100 = gain 40 dB b) gain at the cutoff frequency is 3 dB, so it is 37 dB. c) gain 37 dB = amplification factor 70.7 at the cutoff frequency. |
| back |
Search Engine |
home |