

| Deutsche Version |
| Question: What is the formula for the phase of a sine wave? There is no phase of a sine wave. A sine wave has no phase. A phase can only develop between two sine waves. Two sine waves are mutually shifted in phase, if the time points of its zero passages do not coincide. |
| The word phase has a clear definition for two pure traveling AC sinusoidal waves, but not for music signals. All equalizers shift phase with frequency. Without any fixed-point no "shifting" (displacement) is possible. Special tricks: 90° filter with two allpass filters. Phases are always phase differences. Polarity reversal (pol-rev) is never phase shift on the time axis t. Sinusoidal waveforms of the same frequency can have a phase difference. If there is a phase shift (phase difference) or phase delay of the phase angle φ (Greek letter Phi) in degrees it has to be specified between which pure signals (sine waves) this appears. Thus, for example, a phase shift can be between the two stereo channel signals left and right, between the input and output signal, between voltage and current, or between sound pressure p and velocity of the air particles v. |
What is actually an amplitude?
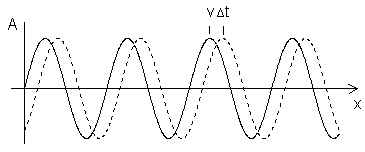
|
One complete cycle of the wave is associated with an "angular" displacement of 2 π radians. The phase φ is the angle of a signal portion, it is specified in angular degrees and provides a reference to the reference value of the entire signal. For periodic signals is the total phase angle of 360 degrees and a period equal to the period duration. A typical question: What is the frequency and the phase angle of a sinusoidal waveform? Does "one" signal can really have a phase? Two "in-phase" waves have a phase (angle) of φ = 0 degrees. If the frequency = 0 Hz, then there is no AC voltage - that's just DC. Then there will be no phase angle present. |
What has time delay to do with phase angle?
| Calculation between phase angle φ° in degrees (deg), the time delay Δ t and the frequency f is: Phase angle (deg) (Time shift) Time difference Frequency λ = c / f and c = 343 m/s at 20°C. Calculation between phase angle φ in radians (rad), the time shift or time delay Δ t, and the frequency f is: Phase angle (rad) "Bogen" means "radians". (Time shift) Time difference Frequency Time = path length / speed of sound |
The time difference (duration) of sound per meter
Effect of temperature on the time difference Δ t
Dependence of the speed of sound only on the temperature of the air
| Temperature of air in °C |
Speed of sound c in m/s |
Time per 1 m Δ t in ms/m |
| +40 | 354.9 | 2.818 |
| +35 | 352.0 | 2.840 |
| +30 | 349.1 | 2.864 |
| +25 | 346.2 | 2.888 |
| +20 | 343.2 | 2.912 |
| +15 | 340.3 | 2.937 |
| +10 | 337.3 | 2.963 |
| +5 | 334.3 | 2.990 |
| ±0 | 331.3 | 3.017 |
| −5 | 328.2 | 3.044 |
| −10 | 325.2 | 3.073 |
| −15 | 322.0 | 3.103 |
| −20 | 318.8 | 3.134 |
| −25 | 315.7 | 3.165 |
| Sound engineers take usually the rule of thumb: For the distance of r = 1 m the sound needs about t = 3 ms in air. Δ t = r / c and r = Δ t × c Speed of sound c = 343 m/s at 20°C. |
| Phase difference φ° (deg) |
Phase difference φBogen (rad) |
Frequency f |
Wavelength λ = c / f |
| 360° | 2 π = 6.283185307 | 2000 Hz | 0.171 m |
| 180° | π = 3.141592654 | 1000 Hz | 0.343 m |
| 90° | π / 2 = 1.570796327 | 500 Hz | 0.686 m |
| 45° | π / 4 = 0.785398163 | 250 Hz | 1.372 m |
| 22.5° | π / 8 = 0.392699081 | 125 Hz | 2.744 m |
| 11.25° | π /16= 0.196349540 | 62.5 Hz | 5.488 m |
Conversion: radians to degrees and vice versa
Phase angle: φ° = 360 × f × Δ t
For time-based stereophony Δ t = a × sin α / c
Frequency f = φ° / 360 × Δ t
Phase angle (deg) φ = time delay Δ t × frequency f × 360
If you take the time difference Δ t = path length a / speed of sound c, then we get
Phase difference φ° = path length a × frequency f × 360 / speed of sound c
Please enter two values, the third value will be calculated
Some more help: Time, Frequency, Phase and Delay
| By Lord Rayleigh
(John William Strutt, 3rd Lord Rayleigh, 1907) the duplex theory was shown. This theory contributes to understanding the procedure of "natural hearing" with humans. It is the very simple realization that the interaural time of arrival differences ITD are important at frequencies below 800 Hz as phase differences with the localization direction as ear signals, while at frequencies above 1600 Hz only the interaural level differences ILD are effective. Between the ears the maximum delay amounts to 0.63 ms. Phase differences for individual frequencies can be calculated. |
Phase shifter circuit for phase angles from φ = 0° to 180°
Voltage vectors of the phase shifter
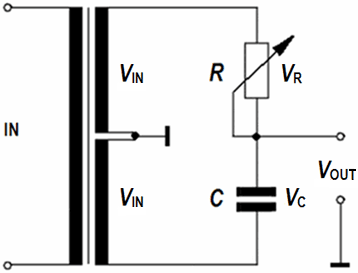 |
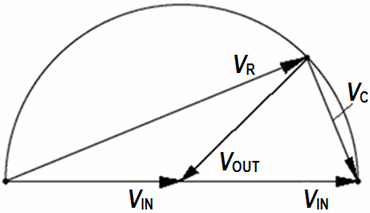 |
For R = 0 ohm is VOUT = VIN. The output should not be loaded by low impedance.
You can shift single pure frequencies (sine waves),
but that is impossible with this schematics for music programs.
Two sine voltages - phase shifted: φ = 45°
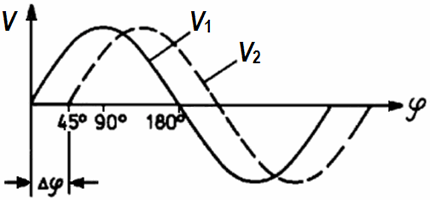 |
Conditions for distortion-free transmission
From Schoeps - Joerg Wuttke: "Mikrofonbuch" - Chapter 7
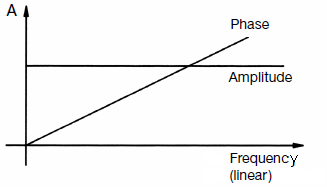 |
| While the demand for a constant frequency response is clear, the "linear" phase needs rather explanation. There are engineers who expect the ideal phase as constant like the amplitude response. That is not true. Initially, the phase begins at 0° because the lowest frequency ends at 0 Hz, at DC. (There is no phase angle between DC voltages). In the course at a given frequency a phase angle is without meaning, if the phase angle is only twice as large in the case of double frequency, and three times as large in triplicate, etc. |
Courtesy of David Moulton Laboratories
(About Comb Filtering, Phase Shift and Polarity Reversal)
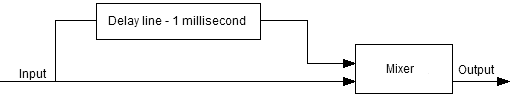 |
| Electronic equivalent of the flow of a signal and its delayed iteration, recombined into a single signal. In the case we will be looking at, the delay line has a delay of 1 millisecond, the levels of both the original and delayed signals going into the mixer are equal, and the signal is a 1 kHz sine wave. |
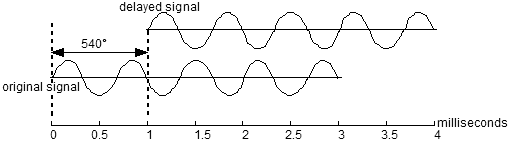 |
|
A sine wave of 1500 Hz. frequency (period T = 0.667 ms) and its delayed iteration, at 1 ms delay. The resulting mixed signal will be a signal with no amplitude, or a complete cancellation of signal. |
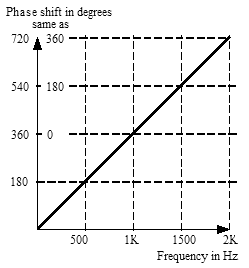 |
| The phase shift for any frequency with a delay of 1 millisecond. The diagonal line represents the increasing phase shift as a function of frequency. Note that we can think of 540° as being effectively the same as 180°. |
Time, Phase, Frequency, Delay - An audio signal theory primer/refresher
Polarity reversal is no Phase shift of 180° (time delay)
| Ř (phi) = phase shift, phase shifting, phase difference, displacement of phase, phase lag, phase angle are often not correct used as:pol-rev = polarity reversal. |
| "It was the nightingale, and not the lark". From: Romeo and Juliet, Act 3, Scene 5, William Shakespeare. It is the "POL-REV" button (polarity reversal) and not the "Phase (shift)" button. 1. Generating a comb filter response 2. "Polarity" and "Phase" |
Polarity and phase are often used as if they mean the same thing. They are not.
The "phase reverse button" does not change the phase. It reverses the polarity.
| Polarity reversal is no phase shift. Polarity reversal (or Pol-Rev) is a term that is often confused with phase Ø (phi) but involves no phase shift or time delay. Polarity reversal occurs whenever we "change the sign" of the amplitude values of a signal. In the analog realm this can be done with an inverting amplifier, a transformer, or in a balanced line by simply switching connections between pins 2 and 3 (XLR plug) on one end of the cable. In the digital realm, it is done by simply changing all pluses to minuses and vice versa in the audio-signal data stream. |
Two sawtooth oscillations
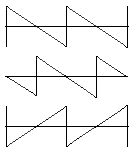 |
top: the original signal a/b (saw tooth) middle: the 180° phase shifted signal as T/2 time shifted sawtooth bottom: the b/a-polarity reversed (inverted) signal, mirrored on the time axis |
| Clearly can be seen that reversed polarity cannot be the same as out of phase. |
| It is about the much-discussed topic: "Phase shift vs. inverting a signal" and "phase shift vs. time shift of a signal." The term phase shift is supposedly defined only for mono frequency sine signals and the phase shift angle is explicitly defined only for sinusoidal quantities. |
The typical Ø (phi)-button is only a polarity changer
There is absolutely no phase shifting
| Note: Time, frequency and phase belong close together. The height of the amplitude has no influence on those parameters. |
| Another thing is the 6 dB per octave roll-off of an electronic RC filter circuit which is damping the amplitude by 3 dB at the cutoff frequency. The phase shift is there always 45°. RC Filter and Cutoff frequency: http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-RCpad.htm Frequency response and equalization EQ: http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-timeconstant.htm Phase and amplitude: Filter (RC pad) with 6 dB per octave http://www.sengpielaudio.com/FilterMit6dBproOktave.pdf |
The Angular Frequency is ω = 2π × f
| Given is the equation: y = 50 sin (5000 t) Determine the frequency and the amplitude. Answer: The amplitude is 50 and ω = 5000. So the frequency is f = 1/T = ω / 2 π = 795.77 Hz. |
| To use the calculator, simply enter a value. The calculator works in both directions of the ↔ sign. |
| back |
Search Engine |
home |