

| English version |
Die quadratischeGleichung hat in ihrer allgemeinen Form
![]()
die beiden Lösungen
Die Normalform einer quadratischen Gleichung lautet
x2 + p · x + q = 0
mit reellen oder komplexen Zahlen p und q. Dabei heißen
x² = quadratisches Glied,
p · x = lineares Glied und
q = absolutes Glied der Gleichung.
Im normierten Fall, der sich durch Division beider Seiten der Gleichung durch a erreichen lässt,
![]()
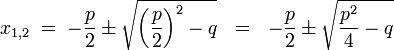
Beispiele für einfache Aufgaben:
| Gleichung | 1. Lösung | 2. Lösung |
| x2 − 2x − 8 = 0 | −2 | 4 |
| 2x2 + 3x − 20 = 0 | −4 | 2,5 |
| 2x2 + 18 = 0 | −9 | 0 |
| x2 + 5x − 14 = 0 | −7 | 2 |
| 3x2 + 36x − 39 = 0 | −13 | 1 |
| 9x2 − 82x + 9 = 0 | 1/9 | 9 |
| 8x2 + 39x − 5 = 0 | −5 | 1/8 |
| 6x2 − 12x − 6 = 0 | 2,414 | −0,414 |
| 2,5x2 + 17,5x − 20 = 0 | −8 | 1 |
| 49x2 + 154x + 21 = 0 | −3 | −1/7 |
| 4x2 + (107/3)x − 3 = 0 | −9 | 1/12 |
| 2x2 − 20,8x + 8 = 0 | 2/5 | 10 |
| 12x2 + x − 1 = 0 | −1/3 | 1/4 |
| 3x2 + 9x − 12 = 0 | −4 | 1 |
| 5x2 − 2x − 3/5 = 0 | −1/5 | 3/5 |
| x2 − 0,9x + 0,7 = 0 | −0,5 | 1,4 |
| 5x2 − 16,5x + 13 = 0 | −2 | −1,3 |
| 0,5x2 − 8x + 32 = 0 | 8 | 8 |
|
Die erste Binomische Formel: (a + b)² = a² + 2ab + b² Die zweite Binomische Formel: (a − b)² = a² +2ab − b² Die dritte Binomische Formel: (a + b) · (a − b) = a² − b² |
| zurück |
Suchmaschine |
Startseite |