

| Deutsche Version |
The speed of light in free space (a vacuum) is the speed at which electromagnetic waves propagate.
| To use the calculator, simply enter a value. The calculator works in both directions of the ↔ sign. |
Formulas and equations: c = λ · f λ = c / f = c · T f = c / λ
| When rounding the speed of light to 300,000,000 m/s you get: |
| Frequency |
Wavelength |
| 1 MHz = 1,000,000 Hz = 106 Hz | 300 m |
| 10 MHz = 10,000,000 Hz = 107 Hz | 30 m |
| 100 MHz = 100,000,000 Hz = 108 Hz | 3 m |
| 1000 MHz = 1000,000,000 Hz = 109 Hz | 0.3 m |
| Conversion Chart Frequency to Wavelength |
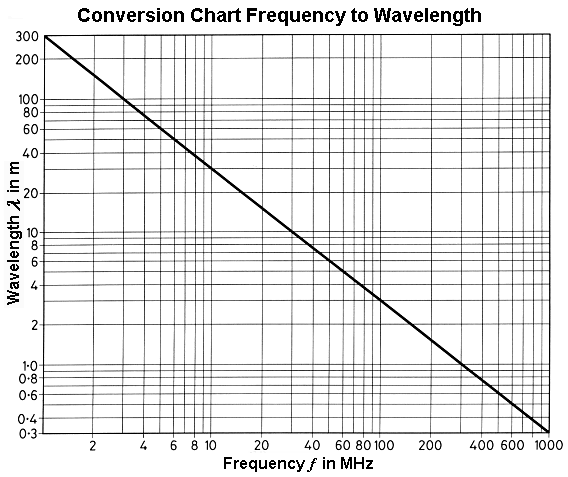 |
| Frequency Bands and Wavelength |
| Worldwide FM radio is operating in VHF band II between 87.5 MHz and 108.0 MHz. |
| Band name | Abbreviation | ITU band | Frequency and wavelength |
Example uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tremendously low frequency | TLF | < 3 Hz > 100,000 km |
Natural and man-made electromagnetic noise | |
| Extremely low frequency | ELF | 3 – 30 Hz 100,000 km – 10,000 km |
Communication with submarines | |
| Super low frequency | SLF | 30 – 300 Hz 10,000 km – 1000 km |
Communication with submarines | |
| Ultra low frequency | ULF | 300–3000 Hz 1000 km – 100 km |
Submarine communication, Communication within mines | |
| Very low frequency | VLF | 4 | 3 – 30 kHz 100 km – 10 km |
Navigation, time signals, submarine communication, wireless heart rate monitors, geophysics |
| Low frequenc | LF | 5 | 30 – 300 kHz 10 km – 1 km |
Navigation, time signals, AM longwave broadcasting (Europe and parts of Asia), RFID, amateur radio |
| Medium frequency | MF | 6 | 300 – 3000 kHz 1 km – 100 m |
AM (medium-wave) broadcasts, amateur radio, avalanche beacons |
| High frequency | HF | 7 | 3–30 MHz 100 m – 10 m |
Shortwave broadcasts, citizens' band radio, amateur radio and over-the-horizon aviation communications, RFID, Over-the-horizon radar, Automatic link establishment (ALE) / Near Vertical Incidence Skywave (NVIS) radio communications, Marine and mobile radio telephony |
| Very high frequency | VHF | 8 | 30–300 MHz 10 m – 1 m |
FM, television broadcasts and line-of-sight ground-to-aircraft and aircraft-to-aircraft communications. Land Mobile and Maritime Mobile communications, amateur radio, weather radio |
| Ultra high frequency | UHF | 9 | 300 – 3000 MHz 1 m – 100 mm |
Television broadcasts, microwave ovens, microwave devices/communications, radio astronomy, mobile phones, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, ZigBee, GPS and two-way radios such as Land Mobile, FRS and GMRS radios, amateur radio |
| Super high frequency | SHF | 10 | 3 – 30 GHz 100 mm – 10 mm |
Radio astronomy, microwave devices/communications, wireless LAN, most modern radars, communications satellites, satellite television broadcasting, DBS, amateur radio |
| Extremely high frequency | EHF | 11 | 30 – 300 GHz 10 mm – 1 mm |
Radio astronomy, high-frequency microwave radio relay, microwave remote sensing, amateur radio, directed-energy weapon, millimeter wave scanner |
| Terahertz or Tremendously high frequency | THz or THF | 12 | 300–3,000 GHz 1 mm – 100 μm |
Terahertz imaging – a potential replacement for X-rays in some medical applications, ultrafast molecular dynamics, condensed-matter physics, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy, terahertz computing/communications, sub-mm remote sensing, amateur radio |
| German radio stations streaming live on the internet: http://www.listenlive.eu/germany.html |
| back |
Search Engine |
home |